Calcitonin: What It Is and When It's Used
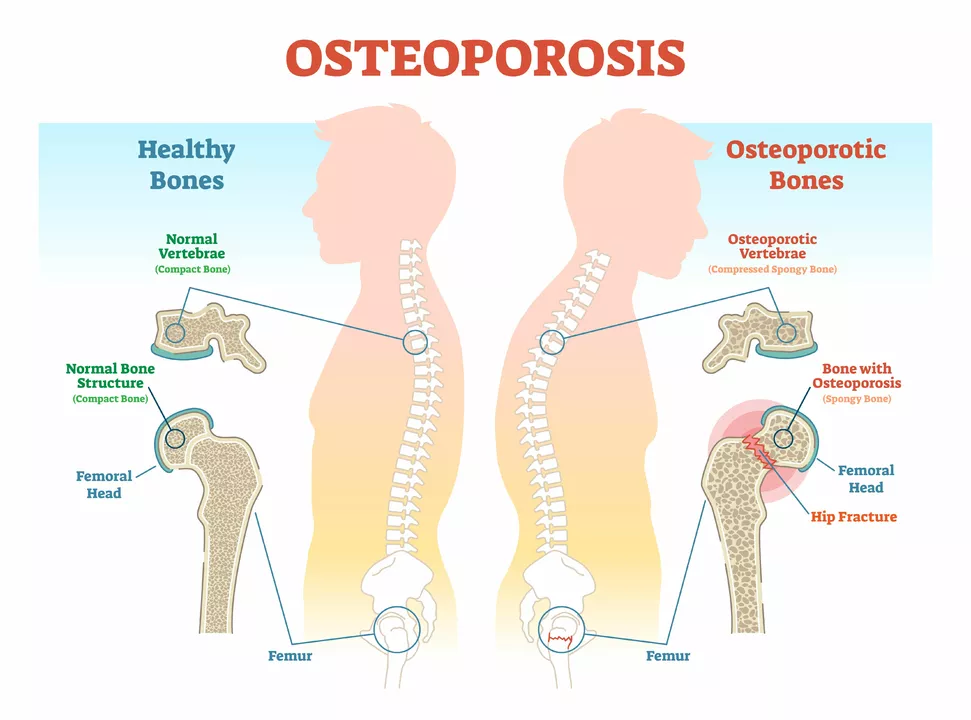
Calcitonin is a hormone that helps control calcium levels in the blood. Doctors use synthetic calcitonin to treat certain bone and calcium disorders, most commonly osteoporosis, Paget’s disease, and acute high calcium (hypercalcemia). It comes as a nasal spray or an injection. The nasal spray contains salmon calcitonin and is the form many patients use long term; injections are often used in hospitals for faster effect.
You might get calcitonin when bisphosphonates or other first-line drugs are unsuitable. For example, some people with swallowing problems or severe kidney issues may tolerate calcitonin better. It lowers bone breakdown by slowing osteoclasts, the cells that remove bone. Expect modest benefit for bone pain and bone loss; other drugs usually work better to prevent fractures.
Common side effects are nausea, flushing, and injection site reactions. The nasal spray can irritate the nose, cause runny nose, or lead to headaches. Rarely, people have allergic reactions—if you develop hives, breathing trouble, or face swelling, stop and seek medical help. Long-term use may slightly increase cancer risk in some studies, so doctors usually limit duration and check risks before continuing therapy.
How you take it matters. Nasal calcitonin is typically used once daily, alternating nostrils as instructed. Injection dosing varies by reason and setting; hospitals use higher doses for severe hypercalcemia. Always follow your prescriber’s directions. Don’t mix doses between nasal and injectable forms without clear medical advice.
Talk with your doctor about interactions and safety. Calcitonin doesn’t interact heavily with many common drugs, but tell your provider about all prescriptions, supplements, and calcium or vitamin D use. If you have allergies to fish proteins, mention that too—salmon-derived products could trigger reactions in sensitive people.
Monitoring is straightforward. Your doctor will watch symptoms, check calcium and kidney tests, and may order bone density scans for long-term use. If you notice increased bone pain, repeated nosebleeds with the spray, or signs of low calcium like muscle cramps, report them right away.
Alternatives are available and often preferred. Bisphosphonates, denosumab, and hormone-related therapies tend to offer stronger fracture protection. Use calcitonin when other options aren’t suitable, or for short-term symptom relief, like acute bone pain.
Buying and storing: keep nasal spray at room temperature and follow product instructions. Injections should be stored according to the pharmacy label and handled by trained professionals. Never share prescription medication.
If you’re wondering whether calcitonin fits your treatment plan, ask your doctor these three quick questions: Why this drug for me? How long will I use it? What side effects should I watch for? That checklist makes the decision clearer and helps you avoid surprises.
Who shouldn’t use calcitonin?
People with known allergy to calcitonin or salmon should avoid it. Pregnant or breastfeeding women need a doctor’s OK — the safety data is limited. Also, if you have very low calcium to begin with, calcitonin could make symptoms worse. Always check with your prescriber if you plan to become pregnant or if you have fluctuating kidney function. Discuss benefits and risks openly.